Application of MRI visualization of nanoprobes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases
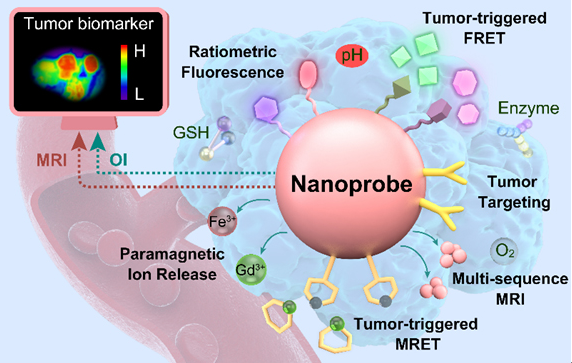
MRI Visualization nanoprobe is a method for visualizing nanoparticles using magnetic resonance imaging (magnetic resonance imaging, MRI) technology, which can be used to detect and image different diseases in living organisms, such as tumors, infection, inflammation, etc. The advantages of MRI visualization nanoprobes are high resolution, high sensitivity, no radiation, no background signal, which can provide multi-functional information, helping to realize the early diagnosis of disease, molecular typing, treatment evaluation and individualized treatment. There are many kinds of MRI visualization nanoprobes, which can be classified according to their responsiveness to different stimuli in an organism, such as pH responsive, reduction responsive, enzyme responsive, temperature responsive, etc. Among them, the tumor microenvironment-responsive MRI visualization nanoprobe is a nanoprobe that can sense and reflect the microenvironment differences between tumor tissue and normal tissue, such as pH value, oxygen concentration, reducing substances, enzymes, etc. Detection and imaging of tumor acidic environment were achieved using fluorine-19 (19F) nuclear-based tumor microenvironment-responsive MRI visualization nanoprobes. This technique uses a polymer containing 19F atoms to wrap iron oxide nanoparticles, which is closed in normal tissue and does not produce 19F signal. and structural changes in tumor tissue due to the decrease of pH, releasing 19F atoms and producing a strong 19F signal, realizing specific imaging of the acidic environment of the tumor. The technology can also be combined with anti-tumor drugs to achieve the integration of tumor diagnosis and treatment.
Reference Documentation:
[1]Li, L.; Chen, F.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Gao, M. Nanoprobes for in vivo magnetic resonance imaging of cancer: A review. Chinese Chemical Letters 2020, 31 (9), 2243-2252.
[2]Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhao, M.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Gao, M. Recent advances in magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents for the diagnosis of liver diseases. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2019, 9 (6), 1147-1160.
[3]Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhao, M.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Gao, M. Stimuli-responsive magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents: design strategies and applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2018, 6 (40), 6347-6365.
+86-18915413828(WhatsApp&WeChat)
Previous: Intracellular in situ
Next: BK Oncolytic virus pla


