Nankai University Huang Xinglu/Kong Deling/Zhuang Jie AM: Mitochondrial-targeted hybrid nanoenzymes designed by bionics can be used as superoxide scavengers
The use of mimic enzymes to remove excess mitochondrial superoxide (O2•−) is an effective means to treat many diseases. Professor Huang Xinglu, Professor Kong Deling, and Associate Professor Zhuang Jie of Nankai University used protein reconstruction technology and nanotechnology to create an artificial hybrid nanoenzyme.

Key points of this article:
(1) These nanoenzymes use ferritin heavy chain-based protein as the enzyme scaffold and metal nanoparticles as the enzyme active center. They have superoxide dismutase and catalase-like activities and can overcome multiple biological barriers. To target mitochondria.
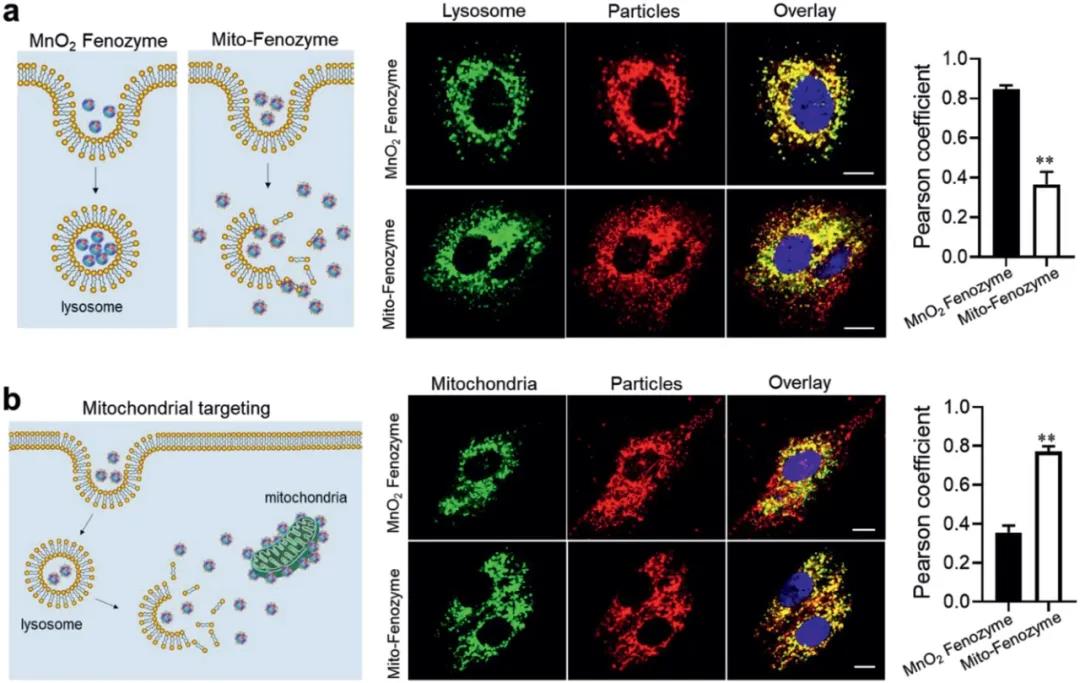
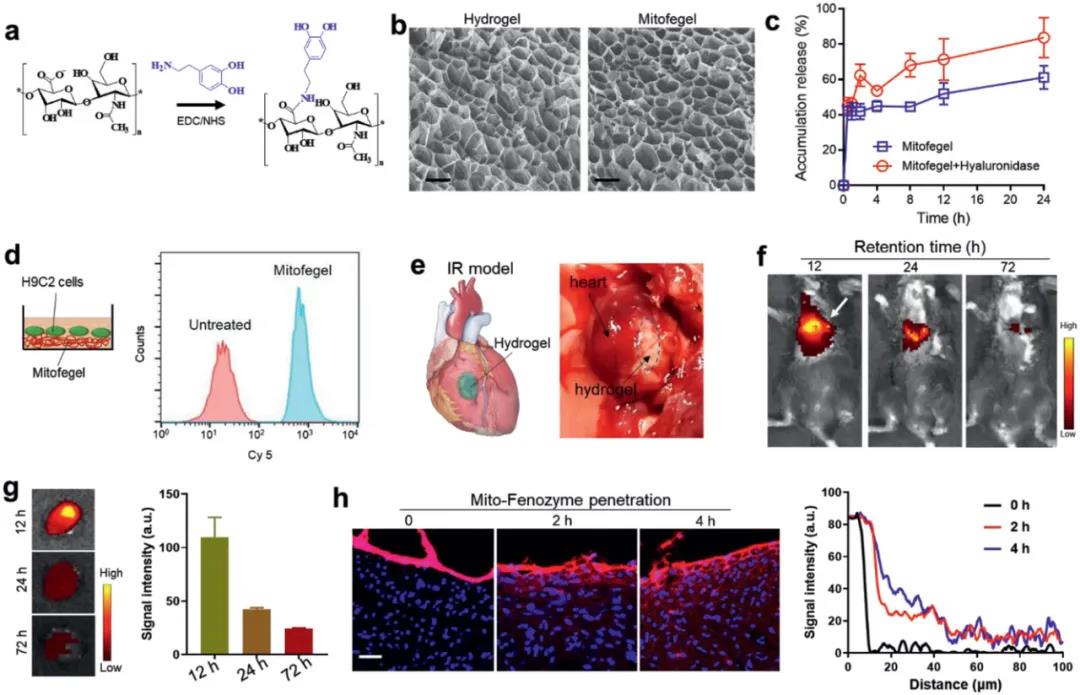
(2) In an animal model of cardiac ischemia-reperfusion, the experiment proved that the hybrid nanoenzyme can damage mitochondria in vivo by oxidative damage and infarction by systemic delivery and local release of adhesive hydrogel (ie, cardiac patch). It plays a protective role during the recovery of heart function. In summary, this study fully clarifies the de novo design strategy for mimic enzymes, and also provides a new type of treatment option for alleviating oxidative damage.
references:
Yue Zhang. et al. Biomimetic Design of Mitochondria-Targeted Hybrid Nanozymes as Superoxide Scavengers. Advanced Materials. 2021
DOI: 10.1002/adma.202006570
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202006570

Key points of this article:
(1) These nanoenzymes use ferritin heavy chain-based protein as the enzyme scaffold and metal nanoparticles as the enzyme active center. They have superoxide dismutase and catalase-like activities and can overcome multiple biological barriers. To target mitochondria.

(2) In an animal model of cardiac ischemia-reperfusion, the experiment proved that the hybrid nanoenzyme can damage mitochondria in vivo by oxidative damage and infarction by systemic delivery and local release of adhesive hydrogel (ie, cardiac patch). It plays a protective role during the recovery of heart function. In summary, this study fully clarifies the de novo design strategy for mimic enzymes, and also provides a new type of treatment option for alleviating oxidative damage.

references:
Yue Zhang. et al. Biomimetic Design of Mitochondria-Targeted Hybrid Nanozymes as Superoxide Scavengers. Advanced Materials. 2021
DOI: 10.1002/adma.202006570
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202006570
+86-18915413828(WhatsApp&WeChat)
Previous: Explore the unknown, t


